Aggregating Measurements
Through aggregation, Sokrates generates new summary views on data.
The input for aggregations and are:
- the file-level measurements (lines of code, history of charges, file age)
- unit-level measurements (lines of code, conditional complexity)
- a list of duplicates within and among the files
- the logical decompositions (each logical decomposition consists of components, and each component of lasts of files in that component)
- concerns (each concern contains the list of files)
- a list of dependencies among components (per logical decomposition)
Sokrates performs aggregation at three levels:
- the overall project level
- the file type level (based on file extension)
- the logical decomposition level
Project-Level Aggregation
Project level aggregations show how data look overall, for all files and units (Figure 1).

Figure 1: An example of system level aggregations.
File-Type Aggregation
File-type level aggregations show how data look for each file extension (Figure 2).

Figure 2: Examples of file extension level aggregations.
Logical-Decomposition Aggregations
Logical-decomposition level aggregations show how data look for each logical decomposition and each component in a logical decomposition (Figure 2).
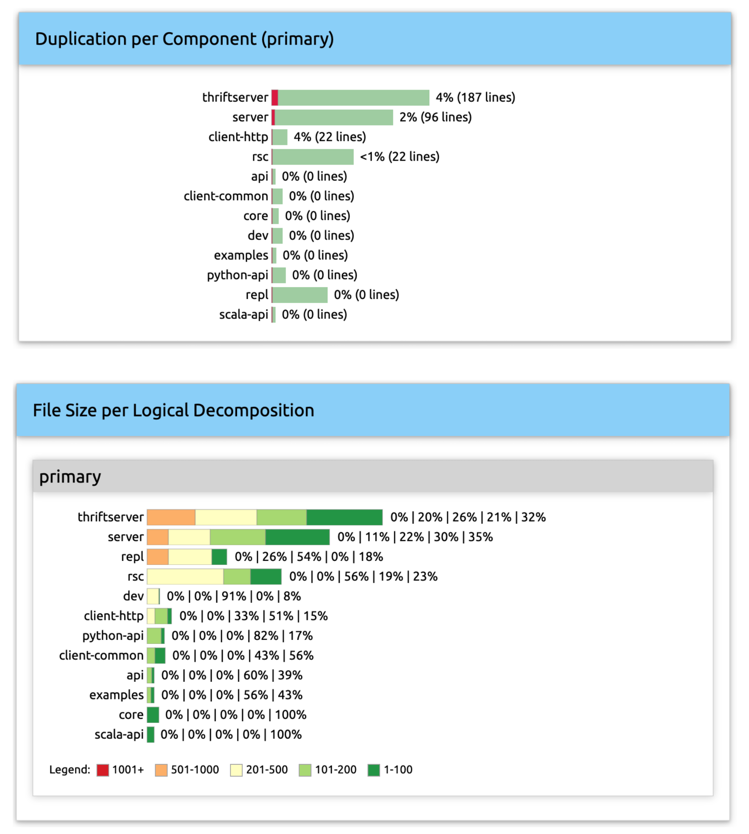
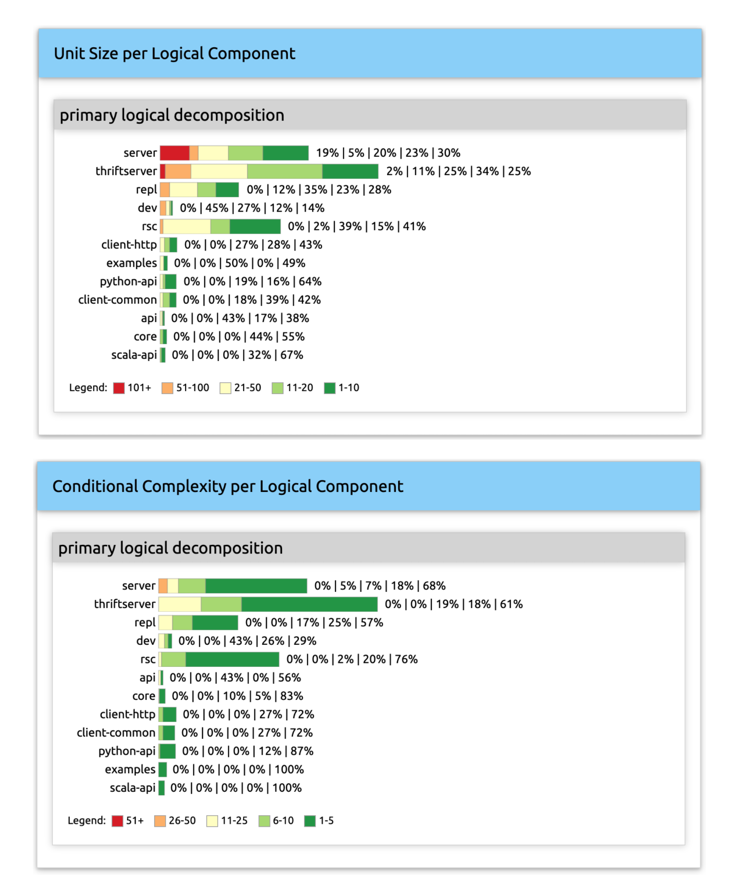
Figure 3: Examples of logical decomposition level aggregations.